What is a filter? Filters are electronic circuits that emphasize certain signals and reject other signals.
What is a crystal filter?
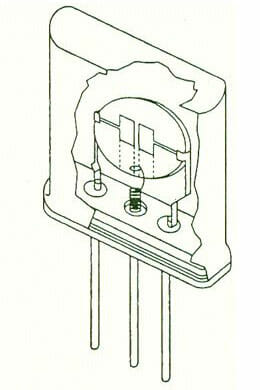
Definition of a Monolithic Crystal Filter: A monolithic (Greek: one stone) crystal filter has 2 sets of electrodes deposited on the same quartz disc. This forms 2 resonators with acoustic (mechanical) coupling between them. If the acoustic coupling is correct a filter response will be achieved.
Typical Construction of a Discrete Crystal and a Monolithic Crystal
Discrete Crystal
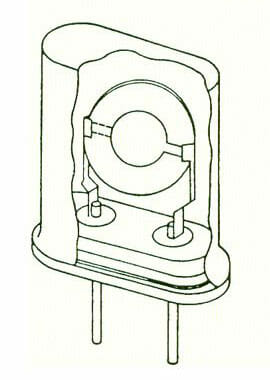
Monolithic Crystal
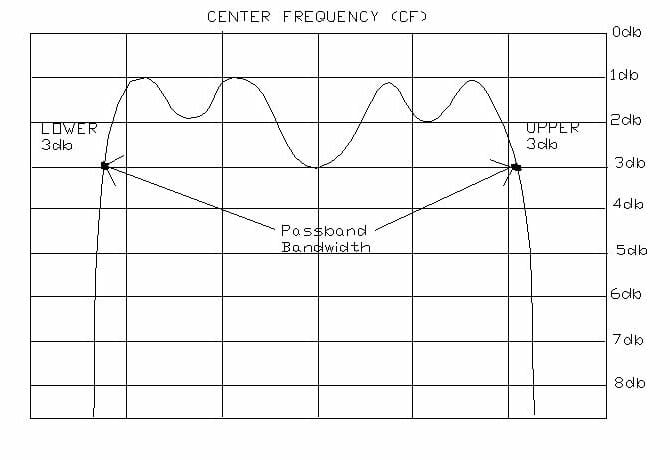
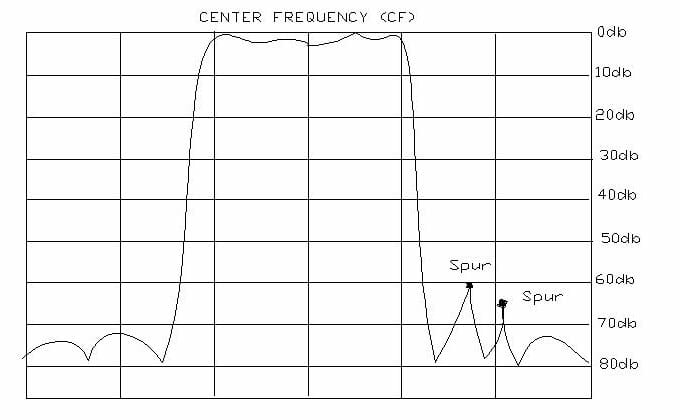
Center Frequency
For bandpass or band reject filters, it is the arithmetic mean of the 3db point frequencies. Also used as the design midpoint of the passband
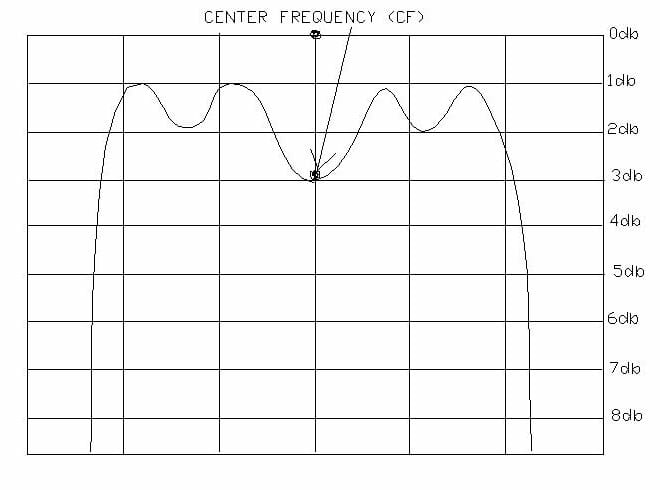
Passband Bandwidth
In a bandpass filter, these limits, or passband edges, are generally the frequencies at which 3db of attenuation is measured. The number if hertz expressing the difference between the upper 3db frequency and lower 3db frequency of a bandpass filter.
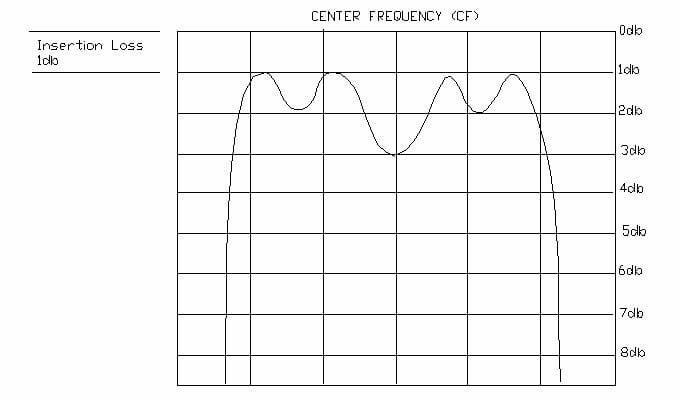
Insertion Loss
The amount of attenuation within the passband of the filter compared to the input signal level. May be measured at center frequency or within 1db passband limits.
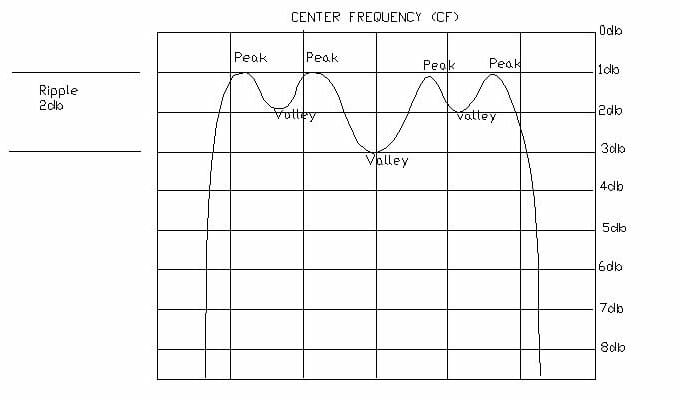
Ripple
The difference in attenuation between the highest peak and the lowest valley within the passband. It is measured in db.
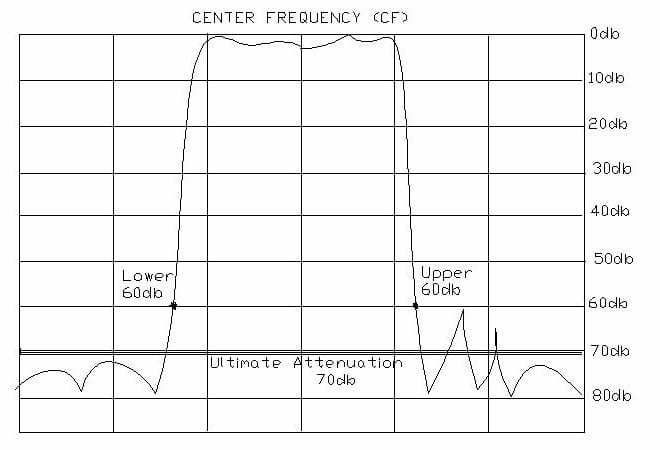
Ultimate Attenuation
The maximum attenuation guaranteed at the specified frequency range.
Spurious Response
Are produced by unwanted vibrational modes in the crystals. Every filter parameter can be moderately to severely distorted by them. They are generally located on the high frequency side of the passband, and in wideband filters, they can occur even within the passband.
Reasons to use Monolithic Crystal Filter
- Lower cost solution
- Less manufacturing time
- Smaller package size
Crystal Filter Electrical Specifications
Standard/Required Specs. Optional/Custom Specs.
- Center Frequency (an absolute usually in MHz)
- Passband Bandwidth (3db or 6db in Hz)
- In-band Ripple (A maximum in dB)
- Insertion Loss (A maximum in dB)
- Stopband (Max. value in Hz @ 30dB, 60dB, etc.)
- Ultimate Attenuation (A minimum in dB) Group Delay (in Seconds)
- Number of Poles
- Spurious Attenuation (A minimum in dB)
- In/Out Impedance (In ohms, typically +/-10%)
- In/Out Capacitance (Typically in picofarads)
Crystal Filter Applications
Where/Who uses them?
- Telecommunication Base Stations
- Radios (Receivers/Transmitters)
- Satellite modem applications (ground based side)
- Radar Applications
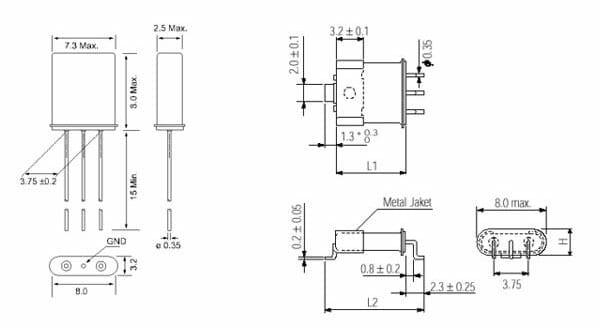
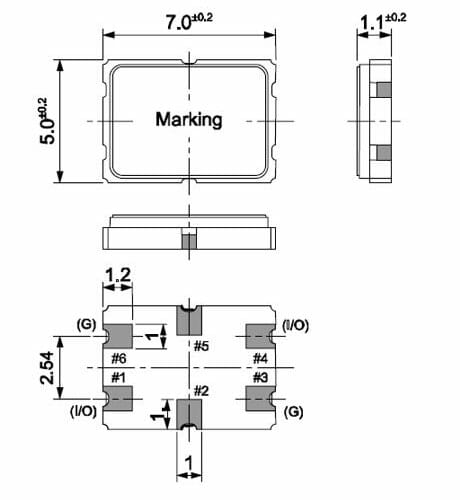
Crystal Filter SMD Package
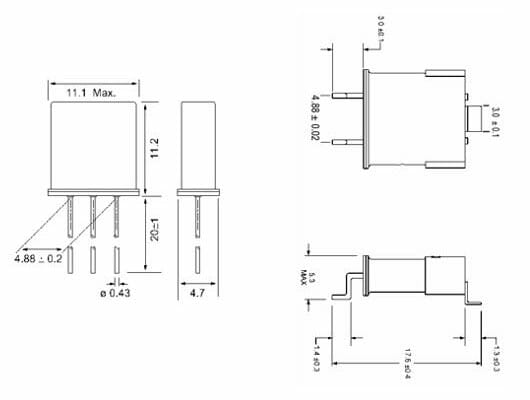
Crystal Filter HC-49 Packages
Crystal Filter UM-1 Packages