Frequency Control Products For Industrial Applications
Welcome to the forefront of industrial innovation with ECS Inc.’s state-of-the-art frequency control products, expertly engineered to meet diverse modern industrial needs. As a leader in frequency control technology, we provide reliable, high-precision components essential for optimizing efficiency, enhancing performance and reducing operational costs. Listed below are a few of the common applications for industrial frequency control components:
- Factory Automation
- Robotics
- Logistics Tracking
- Motor Control
- Building Security
- Communication Systems
- Lighting Control
- Energy Storage Systems
- Drones for Agriculture Management
- Remote Sensing
Explore ECS Inc.’s Product Overview
Explore ECS Inc.’s range of frequency control products designed to propel your operations into the future.
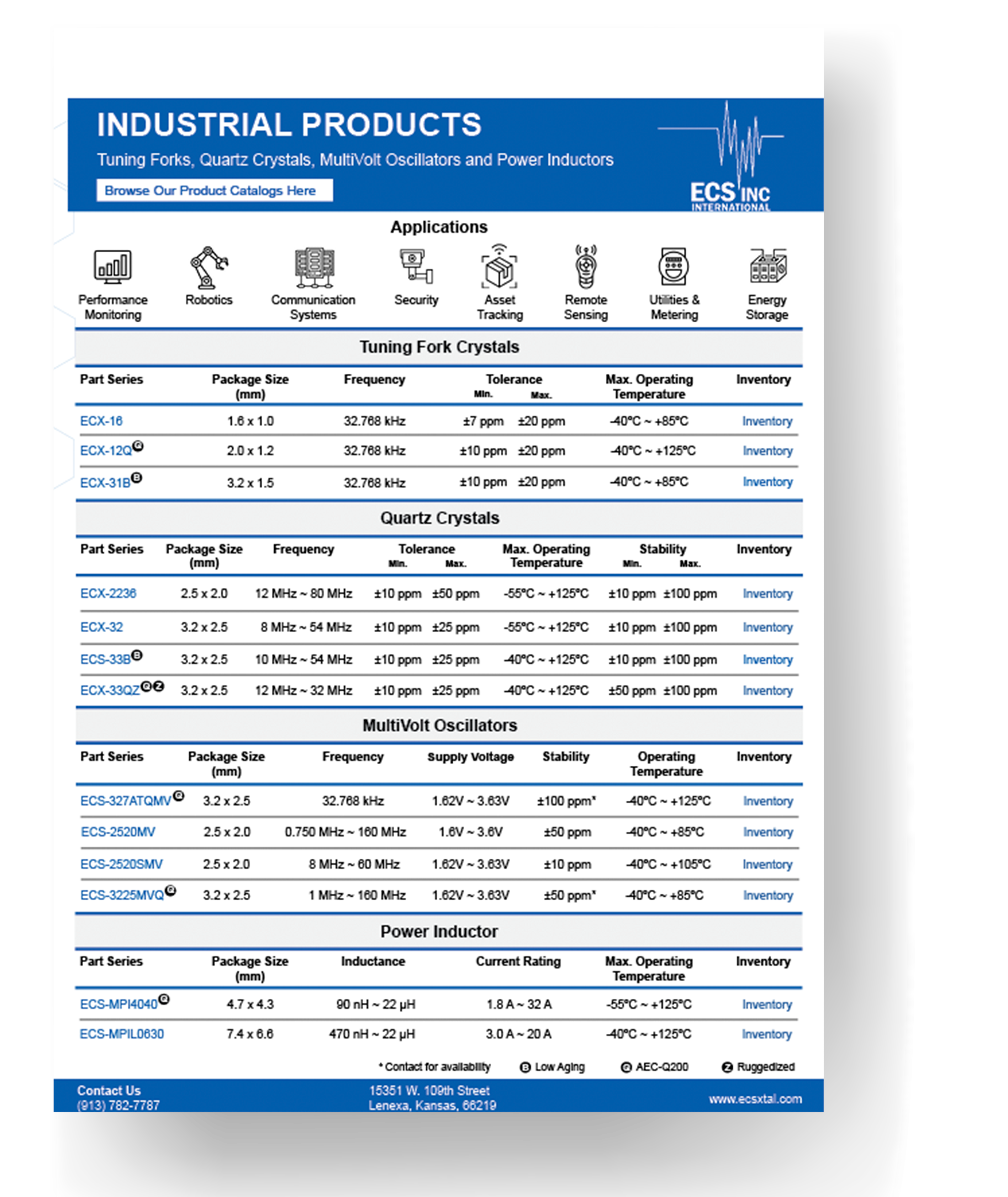
32.768 kHz Tuning Fork Crystals
Surface Mount Crystals
Real Time Clocks (RTC)
MultiVolt Quartz Oscillators
Power Inductors



Enhancing Industrial Automation, Building Control, Renewable Energy and More
By utilizing proper frequency control solutions, you can unlock optimal performance and efficiency tailored for sectors like factory automation, building control, renewable energy and agriculture. ECS Inc.’s products are designed to enhance the reliability of complex machinery, enabling smoother operations and greater productivity.
In factory automation, ECS Inc.’s frequency control devices play a critical role in regulating the timing and synchronizing of conveyor belts, robotic arms and assembly lines, ensuring high-speed production with minimal downtime. Automated handling systems found in warehouse and assembly plants are enhanced by frequency control products by allowing real-time inventory system updates via RFID and IoT technologies, allowing the streamlining of operations and minimized loss costs. For building management systems, frequency control provides the accuracy required for regulating HVAC systems and elevators, ensuring energy efficiency and comfort in commercial and residential buildings.
Transitioning to renewable energy, frequency control solutions are indispensable in stabilizing output from solar panels and wind turbines, facilitating consistent energy supply and effective grid synchronization allowing the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI). Meanwhile, in the agricultural sector, you can enhance your operation of automated feeding systems, IoT livestock tracking and irrigation controls, boosting crop yields and reducing labor costs. Overall, the integration of frequency control components and smart technologies into a wide variety of end use applications opens the door for countless benefits.
Industrial Application Resources
Digital Product Catalogs
Guides